The uncertain nature of the customer demand need to take into consideration by generating the production plan and in particular the production quantities, to meet uncertain customer demand in the best way possible and maximize the profit, by minimizing production costs. Aggregate planning is a process by which a company decides about their ideal levels of capacity, production, inventory, stock-out situations, pricing, subcontracting, etc. Production planning, is the correct placement of production orders concerning place, or region, of production, and time scheduling and sequencing of production orders. The parameters are usually production rate, workforce, overtime, machine capacity level, subcontracting, backlog, and inventory on hand. The amount of overtime production planned is a parameter for aggregate production planning. Production planning for fashion apparel products has to cope with demand uncertainties. Collaborative forecasts created by various enterprises are an important input in aggregate supply chain planning. However, at the time of generating the production plan, the predicted customer demands are largely uncertain.
Category: Supply Chain Management
What is International export and outbound logistics of goods? |
In the international export trade, goods and services, i.e., international export and outbound logistics, goods and services are sold and shipped out of the jurisdiction of the country and customs authorities. While exporting to developed countries, Bangladesh gets some tariff facilities. It is nothing but helping the developing countries in export trade and industrialization, on the other hand, they regulate some products to enter their country at a lower price. Currently, Bangladesh is enjoying tariff-free market access for 90 percent to 100 percent of products in all the developed countries except the United States. Tariff-free and low-tariff market access facilities in developed and some developing countries immensely benefited Bangladesh. Bangladesh High Commissioner to Ottawa wrote that quality of Bangladesh’s apparel products as well as the efficient supply-chain mechanism has largely contributed to doubling bilateral trade in a decade.
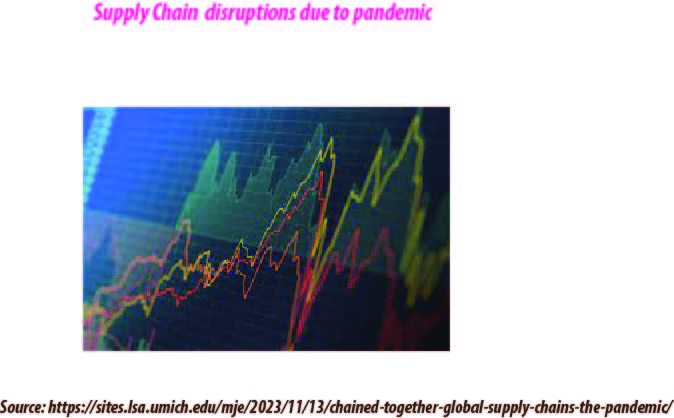
The post Covid-19 Supply Chains: A Brief Discussion |
The U.S.-China trade war and the Covid-19 crisis have prompted manufacturers worldwide to reassess their supply chains, focusing on increasing domestic production, boosting employment in their home countries, reducing dependence on risky sources, and rethinking lean inventories and just-in-time replenishment strategies. The pandemic has exposed vulnerabilities in production strategies and supply chains, leading to increased political and competitive pressures. Modern products often require specialized technological skills, and manufacturers often rely on suppliers and subcontractors who focus on specific areas. However, relying on a single supplier deep in their network increases disruption risks. To mitigate these risks, manufacturers should categorize suppliers as low-, medium-, or high-risk, using metrics like revenue impact, factory recovery time, and alternate sources.
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): Its Effects On Businesses and Brands
Achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) is a critical role for businesses and brands, as it can have a big impact on their operations, strategies, branding, and stakeholder interactions. In order to meet global sustainability goals, promote innovation in goods and services as well as business models, and draw in socially conscious clientele, companies are incorporating the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) into their plans. ESG factors are also being considered by investors when making decisions, and businesses that support the SDGs stand to gain access to sustainable finance sources and a greater number of investments.
Goals such as “Climate Action” and “Responsible Consumption and Production” can encourage companies to streamline their supply chains, cut waste, and use more environmentally friendly production techniques. Governments are putting SDG-aligned laws into effect, and businesses need to follow them to avoid fines or reputational harm.
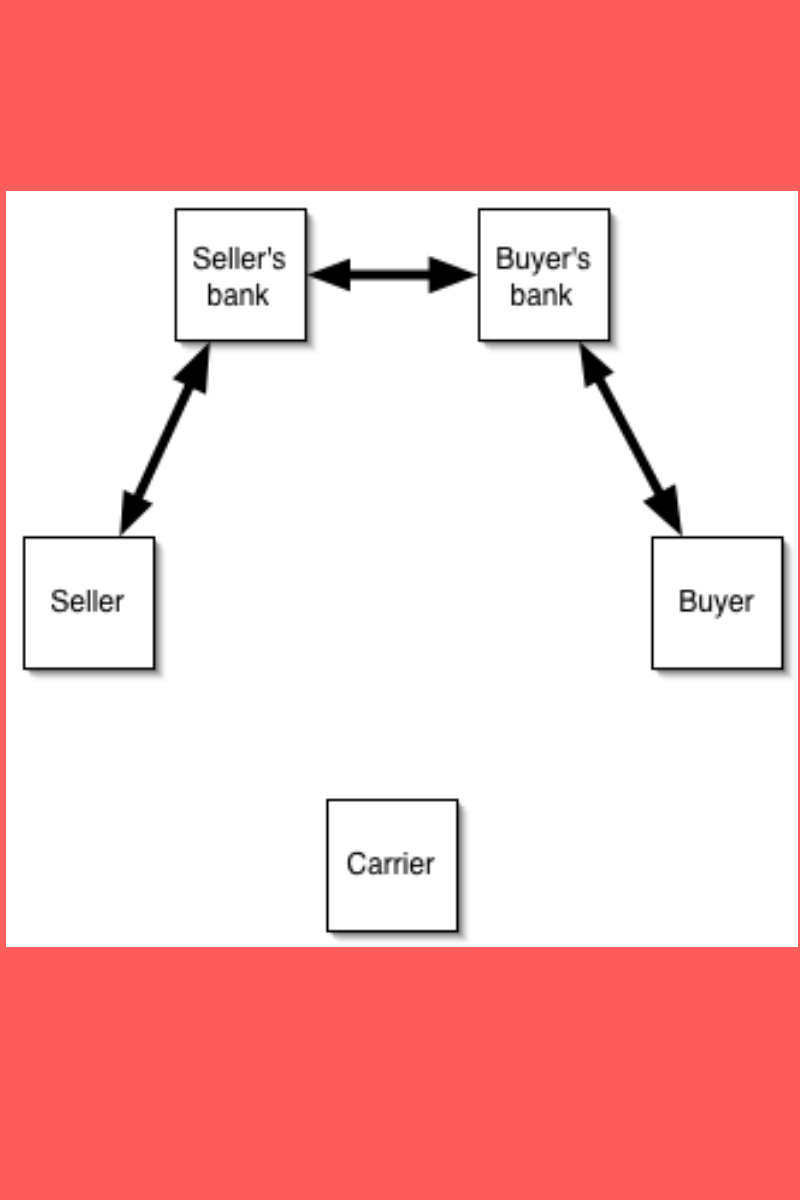
Letter of Credit and Blockchain Technology In A Supply Chain |
A letter of credit(LC) is also named a documentary credit(DC) in globalized international trade. In recent times, banks utilize blockchain technology regarding the formulation of letters of credit . The ICC regulates market practices (Documentary Credit 600). These include the advising bank that will give the documentary credit to the beneficiary or their nominated bank and provide their nominated bank with any amendments to the letter of credit. The bank retains a certain percentage of the letter of credit value for security. Blockchain technology is available for the letter of credit procedure and trade finance is related to it. Commerce and international trade finance include products such as issuing letters of credit, indemnifying Bills of Lading, etc. Although the letter of credit was created in the old world, methods managing the shipping of goods and related accommodations. But there is a great potential to supersede these paper processes with digitized operations utilizing blockchain technology. International trade requires a number of participants to interact with one another, i.e., the exporters, importers, banks, shipping companies, port-related entities, and customs. Trade finance in supply chain management(SCM) includes products such as lending, issuing letters of credit, factoring, export credit, and indemnification. Therefore, we can say that letter of credit and blockchain technology both are used in A Supply Chain for running international trade safely.
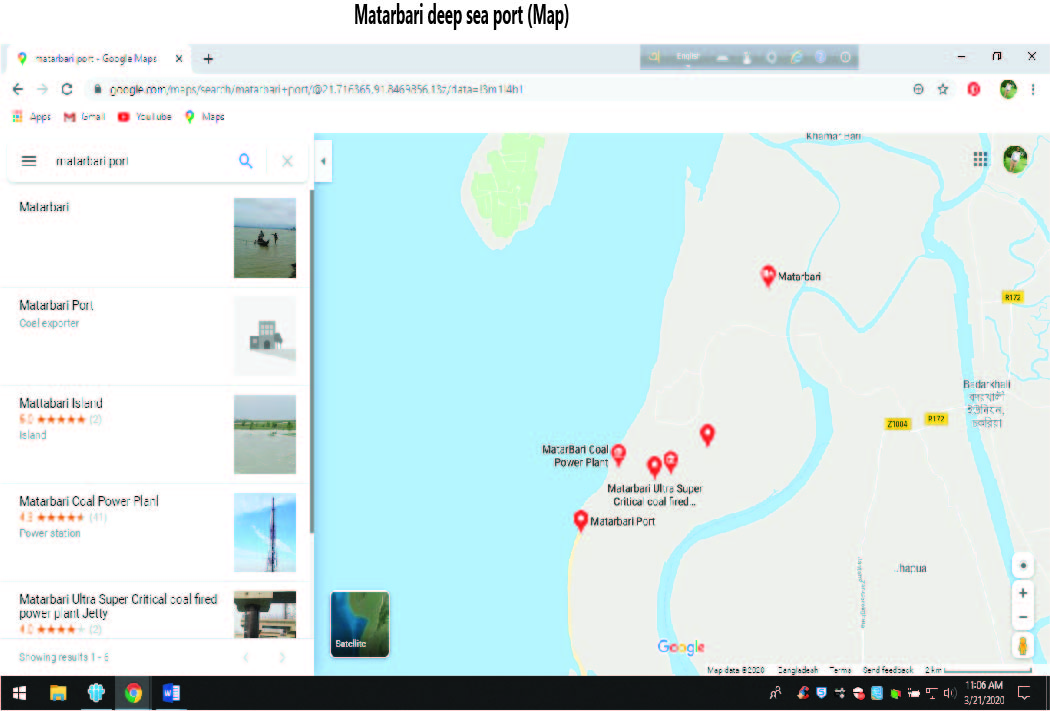
About the Matarbari deep sea port: A Supply Chain Management perspective |
To ensure load unload of deep draft vessels the Matarbari port is essential for Bangladesh and adjacent countries and areas. The Matarbari deep sea port has a 16m depth that will help 16m draft vessels to unload their cargo at the terminal. At deep sea, currently mother vessels unload the cargo at feeder vessel and they carry the cargo to the Chittagong port. The present seaports (Chattogram sea port and Mongla sea port) of the country do not have the capacity to handle huge containers and vessels and the building of a deep sea port is the only solution. Chittagong port can’t load unload from more than 9.5 meter vessels.
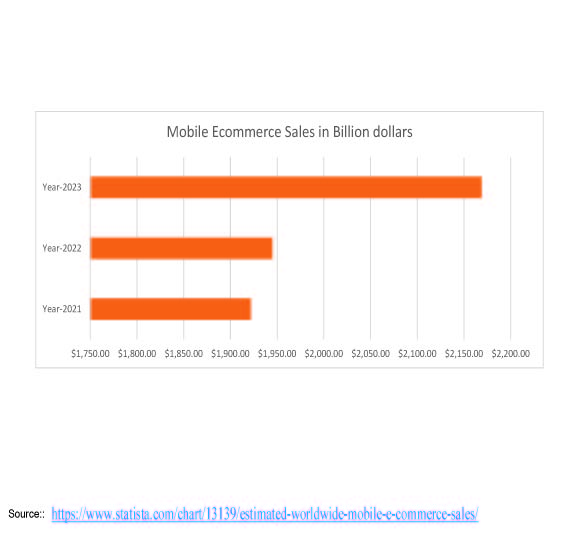
How to explain the rise of ecommerce challenges and opportunities for supply chain management?
The rise of e-commerce has brought significant changes to the global economy, altering industries and consumer behavior. However, it has also presented challenges and opportunities for supply chain management. E-commerce has led to an increase in demand for quick order fulfillment, requiring more sophisticated logistics networks and faster delivery services. Inventory management has become more complex, with the need for real-time visibility and accurate demand forecasting to prevent stockouts and overstocking. Achieving transparency across the supply chain is crucial for accurate and on-time order fulfillment, while managing returns efficiently is important for customer satisfaction and cost control. Integrating supply chain management with e-commerce platforms allows companies to provide a seamless shopping experience with real-time tracking information and multiple delivery options. An agile and responsive supply chain enables companies to adapt quickly to changes in customer demand and external disruptions, ensuring high levels of customer satisfaction and loyalty. By adopting automation and digital technologies, companies can lower costs, increase efficiency, and gain a competitive edge in the fast-paced e-commerce environment. So, there are Ecommerce challenges and opportunities for supply chain management.