Featured Posts
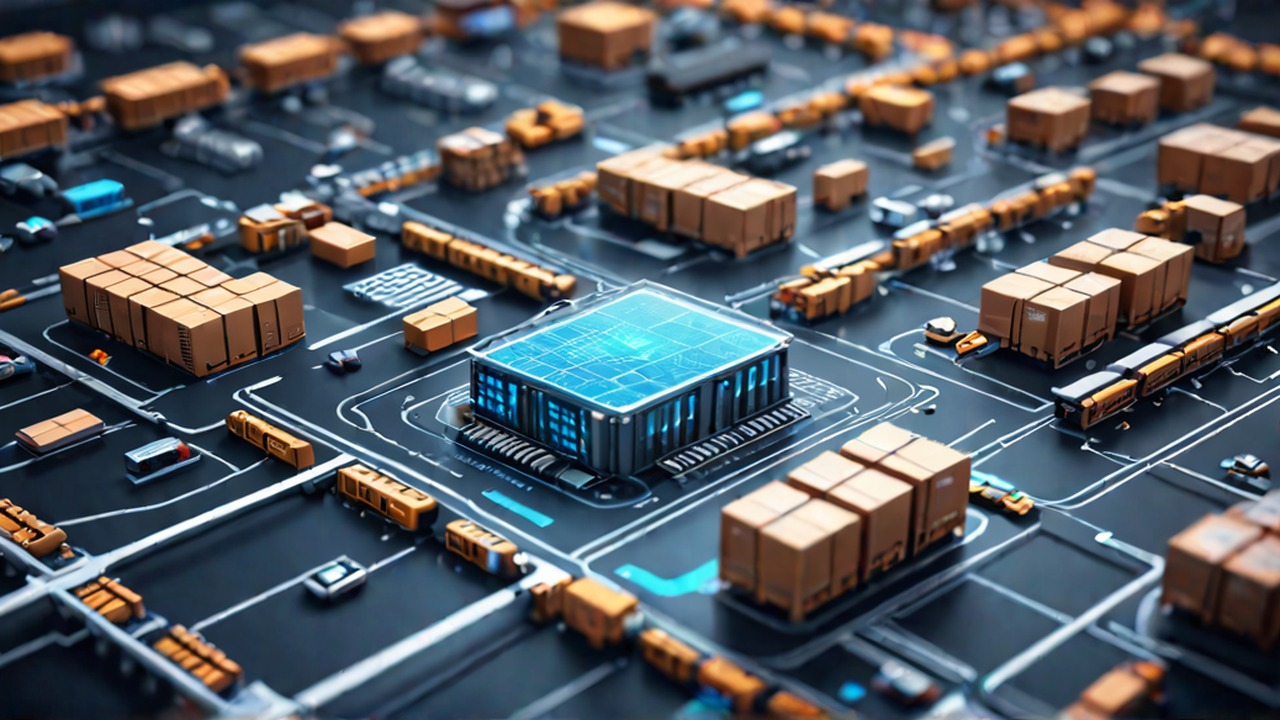
View AllUnveiling Amazon’s Digital Supply Chain Strategies: A Case Study
- ikram
- April 10, 2025
- 0
What is Cycle View of a Supply Chain? Is it Useful? |
- ikram
- December 12, 2024
- 6
A discussion about Unilever’s Supply Chain Management : A Case Study |
- ikram
- December 2, 2024
- 0
How supply chain planning works: A discussion in brief |
- ikram
- November 19, 2024
- 0
What is International export and outbound logistics of goods? |
- ikram
- November 1, 2024
- 0
Trending Posts
View AllUnveiling Amazon’s Digital Supply Chain Strategies: A Case Study
- ikram
- April 10, 2025
- 0
Abstract Amazon’s digital supply chain is a technological marvel, integrating software and hardware to…
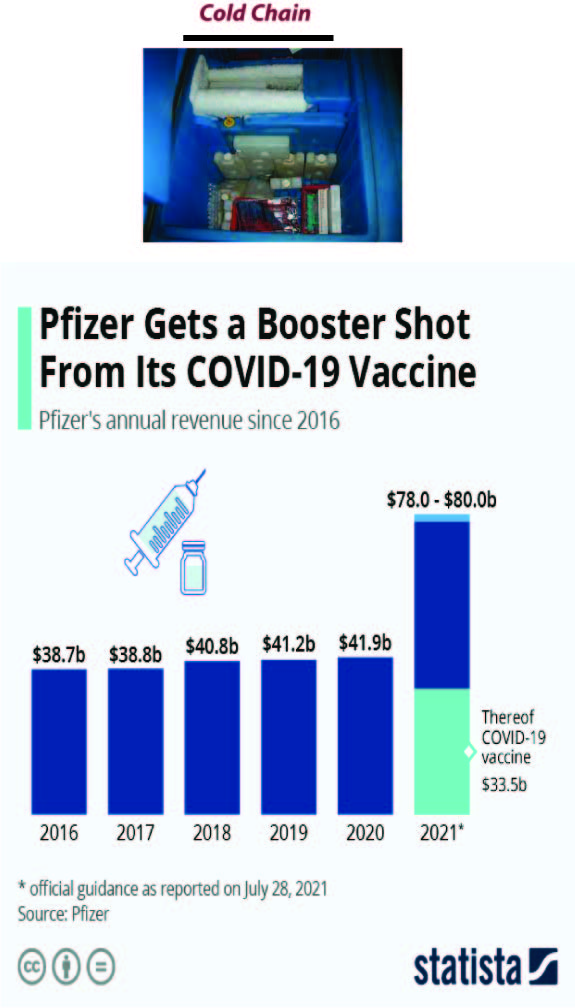
How to Explain Cold Chain as a Supply Chain and Logistical issue? |
- ikram
- March 15, 2025
- 0
Existing amenities are not enough to store, and deliver a large volume of vaccines within…
How Does the International ship and Port Facility Security Code Enhance Supply Chain Security?
- ikram
- March 1, 2025
- 0
Each ship must develop a unique plan to protect against security threats. The plan must…
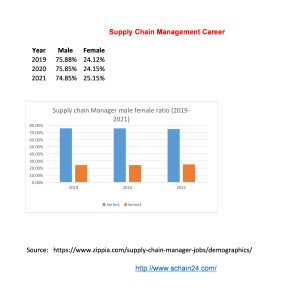
What is a Supply Chain Management Job and Career?
- ikram
- January 27, 2025
- 0
In a case study, based on US-based companies, first-level management is of about 0-4 years.…
Latest Posts
View AllUnveiling Amazon’s Digital Supply Chain Strategies: A Case Study
- ikram
- April 10, 2025
- 0
Abstract Amazon’s digital supply chain is a technological marvel, integrating software and hardware to connect every link of the chain, from suppliers to customers. It uses advanced algorithms and…
The post Covid-19 Supply Chains: A Brief Discussion |
- ikram
- October 15, 2024
- 0
The U.S.-China trade war and the Covid-19 crisis have prompted manufacturers worldwide to reassess their supply chains, focusing on increasing domestic production, boosting employment in their home countries, reducing dependence…
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): Its Effects On Businesses and Brands
- ikram
- October 1, 2024
- 0
Achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) is a critical role for businesses and brands, as it can have a big impact on their operations, strategies, branding, and stakeholder interactions. In…
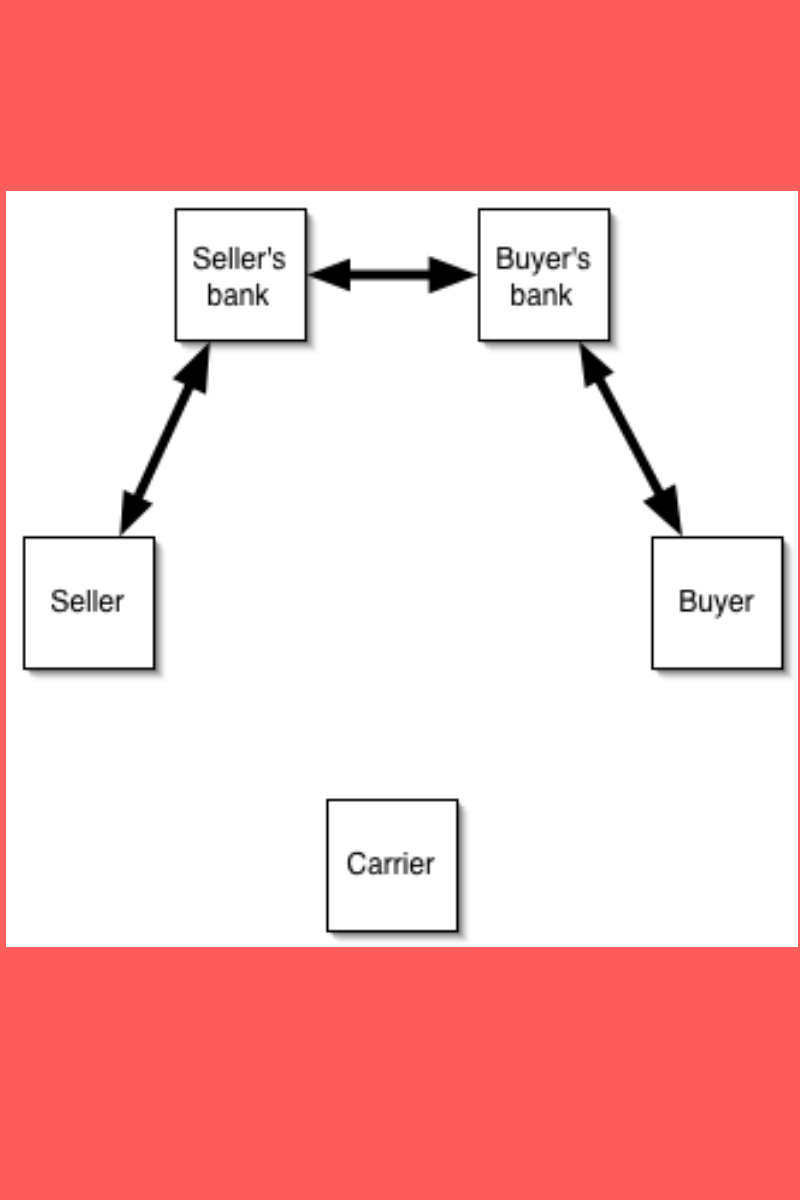
Letter of Credit and Blockchain Technology In A Supply Chain |
- ikram
- September 24, 2024
- 0
A letter of credit(LC) is also named a documentary credit(DC) in globalized international trade. In recent times, banks utilize blockchain technology regarding the formulation of letters of credit . The…
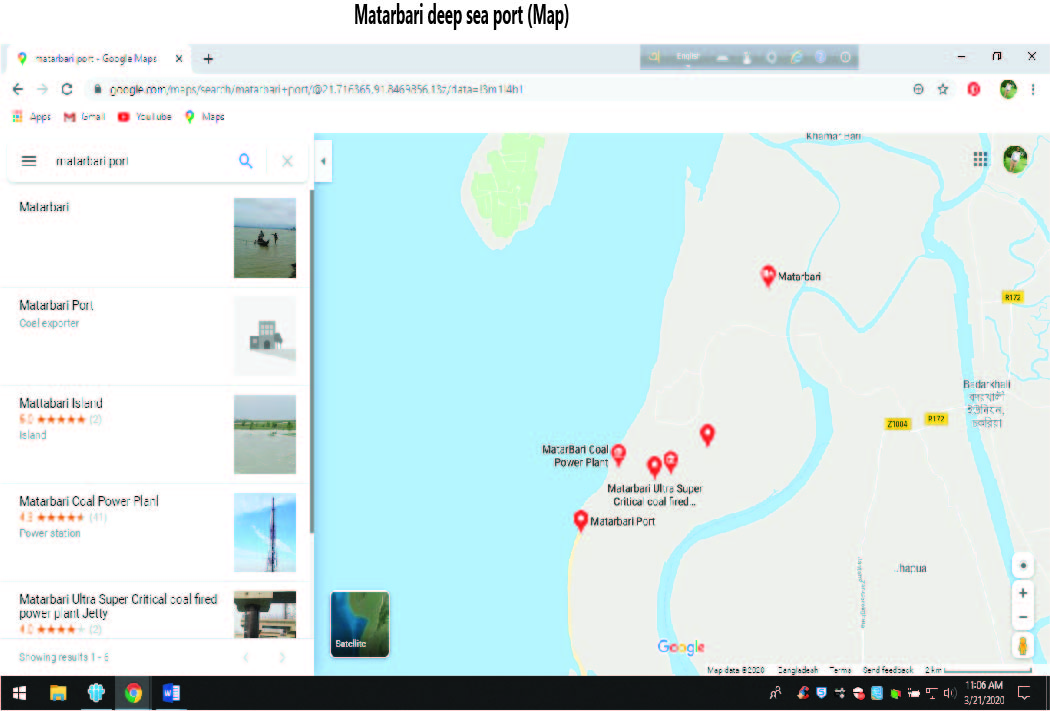
About the Matarbari deep sea port: A Supply Chain Management perspective |
- ikram
- September 15, 2024
- 0
To ensure load unload of deep draft vessels the Matarbari port is essential for Bangladesh and adjacent countries and areas. The Matarbari deep sea port has a 16m depth that…
Supply Chain Management
View AllUnveiling Amazon’s Digital Supply Chain Strategies: A Case Study
- ikram
- April 10, 2025
- 0
Abstract Amazon’s digital supply chain is a technological marvel, integrating software and hardware to connect every link of the…
What is International export and outbound logistics of goods? |
- ikram
- November 1, 2024
- 0
In the international export trade, goods and services, i.e., international export and outbound logistics, goods and services are sold and…
The post Covid-19 Supply Chains: A Brief Discussion |
- ikram
- October 15, 2024
- 0
Letter of Credit and Blockchain Technology In A Supply Chain |
- ikram
- September 24, 2024
- 0
Unveiling Amazon’s Digital Supply Chain Strategies: A Case Study
- ikram
- April 10, 2025
- 0
Abstract Amazon's digital supply chain is a technological marvel, integrating software and hardware to connect every link of the chain, from suppliers to customers. It uses advanced algorithms and…
How to Explain Cold Chain as a Supply Chain and Logistical issue? |
- ikram
- March 15, 2025
- 0
Abstract Existing amenities are not enough to store, and deliver a large volume of vaccines within a short time, say experts. The governments are considering banking on the existing cold…
How Does the International ship and Port Facility Security Code Enhance Supply Chain Security?
- ikram
- March 1, 2025
- 0
Abstract Each ship must develop a unique plan to protect against security threats. The plan must be approved by the ship's flag state. Port facilities must also develop a…
What is a Supply Chain Management Job and Career?
- ikram
- January 27, 2025
- 0
Abstract In a case study, based on US-based companies, first-level management is of about 0-4 years. To understand the supply chain management job and career we can remind ourselves about…
Unveiling Amazon’s Digital Supply Chain Strategies: A Case Study
- ikram
- April 10, 2025
- 0
Abstract Amazon’s digital supply chain is a technological marvel, integrating software and hardware to connect every link of the chain, from suppliers to customers. It uses advanced algorithms and…
What is Cycle View of a Supply Chain? Is it Useful? |
- ikram
- December 12, 2024
- 6
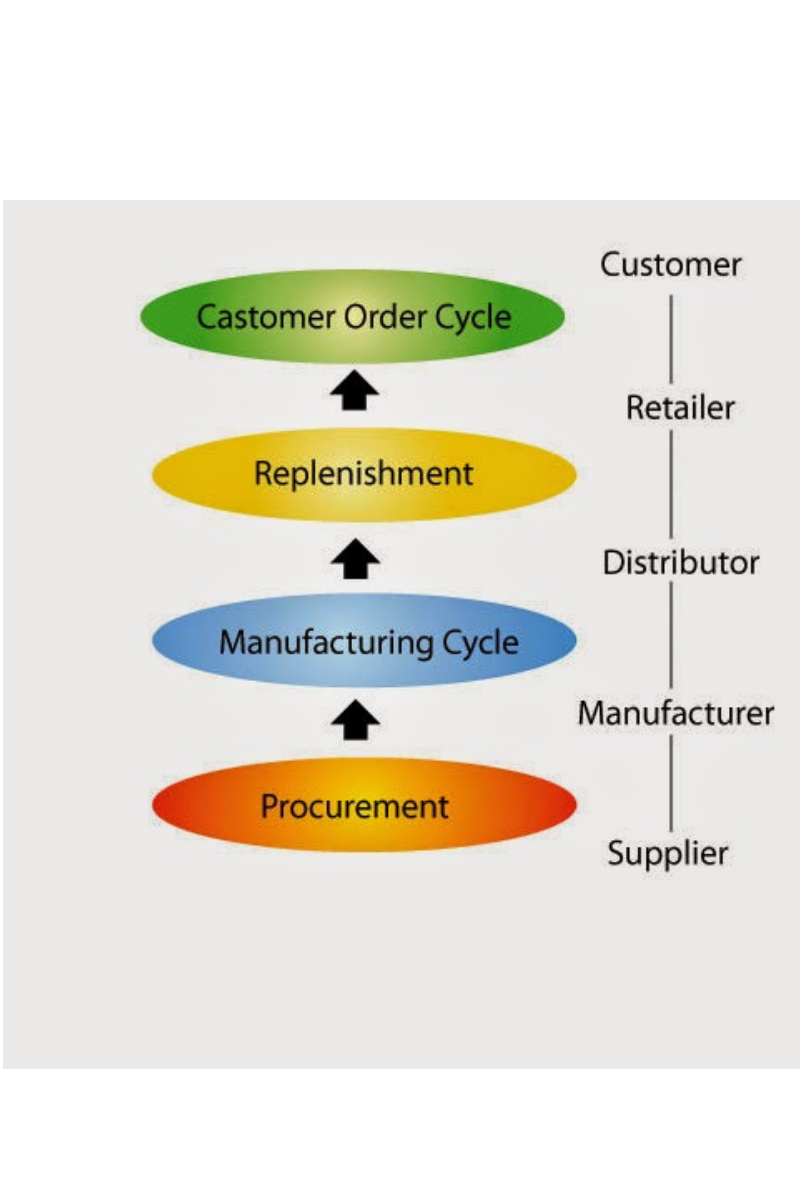
The processes in a Supply Chain are usually divided into a series of cycles, each performed in the interface between two interrelated successive stages of a Supply Chain. Sub-processes in…
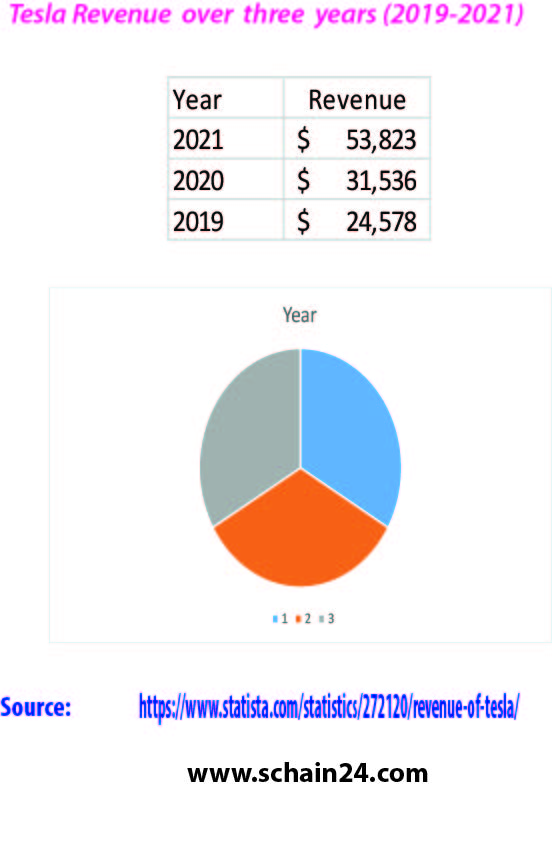
Tesla’s supply chain and logistics: A case study
- ikram
- May 1, 2023
- 0
The company was incorporated as Tesla Motors, Inc. on July 1, 2003, by Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning. Eberhard verbalized he wanted to build a car manufacturer that is additionally…
H & M Supply Chain management: A case study
- ikram
- January 8, 2023
- 0
Hennes & Mauritz AB is a Swedish multinational clothing-retail company known for its fast-fashion clothing for men, women, teenagers, and children. As of November 2019, H&M operates in 74 countries…
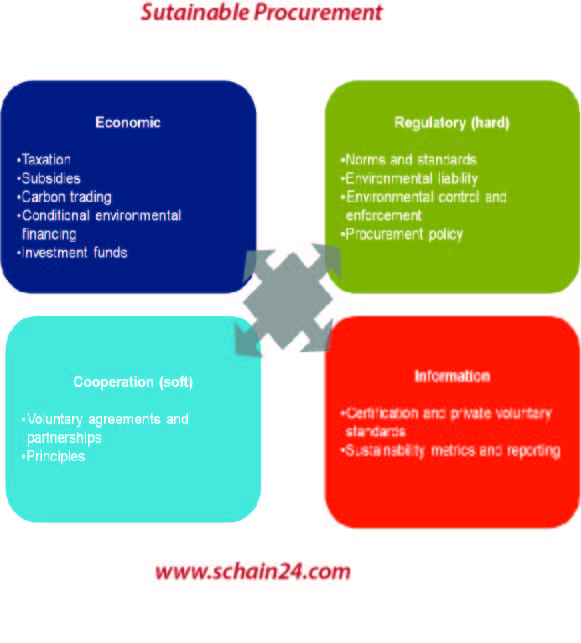
Sustainable Procurement: A Concept Used In SCM And Beyond.
- ikram
- August 2, 2023
- 0
There are different levels of focus in the dimensions of sustainability and also sustainable procurement. Focus on the supply chain network entails managing and balancing the supplier portfolio. The impact…
Trending
View AllHow to Explain Cold Chain as a Supply Chain and Logistical issue? |
- ikram
- March 15, 2025
- 0
What is a Supply Chain Management Job and Career?
- ikram
- January 27, 2025
- 0
What is the Role of Inventory in Supply Chain Management?
- ikram
- January 13, 2025
- 0
Unveiling Amazon’s Digital Supply Chain Strategies: A Case Study
- ikram
- April 10, 2025
- 0
How to Explain Cold Chain as a Supply Chain and Logistical issue? |
- ikram
- March 15, 2025
- 0
What is a Supply Chain Management Job and Career?
- ikram
- January 27, 2025
- 0
What is the Role of Inventory in Supply Chain Management?
- ikram
- January 13, 2025
- 0
Unveiling Amazon’s Digital Supply Chain Strategies: A Case Study
- ikram
- April 10, 2025
- 0
How to Explain Cold Chain as a Supply Chain and Logistical issue? |
- ikram
- March 15, 2025
- 0
What is a Supply Chain Management Job and Career?
- ikram
- January 27, 2025
- 0
What is the Role of Inventory in Supply Chain Management?
- ikram
- January 13, 2025
- 0
Editor’s Picks
View All
Follow Us On
Popular Posts
View AllHow supply chain planning works: A discussion in brief |
- ikram
- November 19, 2024
- 0
What is Cycle View of a Supply Chain? Is it Useful? |
- ikram
- December 12, 2024
- 6
How supply chain planning works: A discussion in brief |
- ikram
- November 19, 2024
- 0
What is Cycle View of a Supply Chain? Is it Useful? |
- ikram
- December 12, 2024
- 6
How supply chain planning works: A discussion in brief |
- ikram
- November 19, 2024
- 0
Recent
View AllUnveiling Amazon’s Digital Supply Chain Strategies: A Case Study
- ikram
- April 10, 2025
- 0
Abstract Amazon’s digital supply chain is a technological marvel, integrating software and hardware to…
How to Explain Cold Chain as a Supply Chain and Logistical issue? |
- ikram
- March 15, 2025
- 0
Existing amenities are not enough to store, and deliver a large volume of vaccines within…
How Does the International ship and Port Facility Security Code Enhance Supply Chain Security?
- ikram
- March 1, 2025
- 0
Each ship must develop a unique plan to protect against security threats. The plan must…
What is a Supply Chain Management Job and Career?
- ikram
- January 27, 2025
- 0
In a case study, based on US-based companies, first-level management is of about 0-4 years.…