Abstract
Package carriers, such as DHL, FedEx, UPS, etc. usually carry letters and other small cargo weighing below 150 pounds using air, Truck, and rail to carry time-sensitive smaller packages. Companies use air cargo carriers for larger cargo and package carriers for more time-sensitive smaller cargo. A carrier takes investment decisions regarding their equipment; Shipper in contrast uses transportation to minimize total cost, while providing an appropriate level of responsiveness to the customers. The Key issues air carriers usually face include identifying the location and a number of hubs, assigning planes to routes, and maintaining a schedule of planes and crews, also available at different prices. The effectiveness of any mode of transportation is affected by the carrier as well as infrastructure and transportation policies, e.g., an airline’s goal is to maximize the daily flying time of a plane and generated revenue per trip. Supply Chains using modes of transportation, such as air, package carriers, trucking, rail, water, pipelines, intermodal, etc. The cargo moves from the factory premises to the port in a truck or multi-modal movement of truck and container on the rail. The shipper requires the movement of products from one point to another in a Supply Chain and Carrier is the party who moves the cargo. AI algorithms can optimize routes for each autonomous vehicle in real-time, based on traffic data, road conditions, and other factors. AI algorithms can mine historical and real-time traffic data to create predictive models to anticipate traffic congestion and accidents. AI will manage the optimum distance between vehicles, maintain constant communication between vehicles, and plan the formation of vehicle clusters to ensure consistent traffic flow and avoid bottlenecks. Air carriers usually carry below 500 pounds, high-value, and lightweight products.
Keyword: transportation.
Introduction
Would like to discuss Transportation issues in the light of Logistics and Supply Chain Management through this article in short. These are terms such as understanding transportation, different modes of transportation, the role of infrastructure and policies, various transportation networks, identifying some points on trade-offs while designing transportation networks, etc. Also, discuss some Bangladesh perspectives after discussing some general transport issues.
Role of Transportation
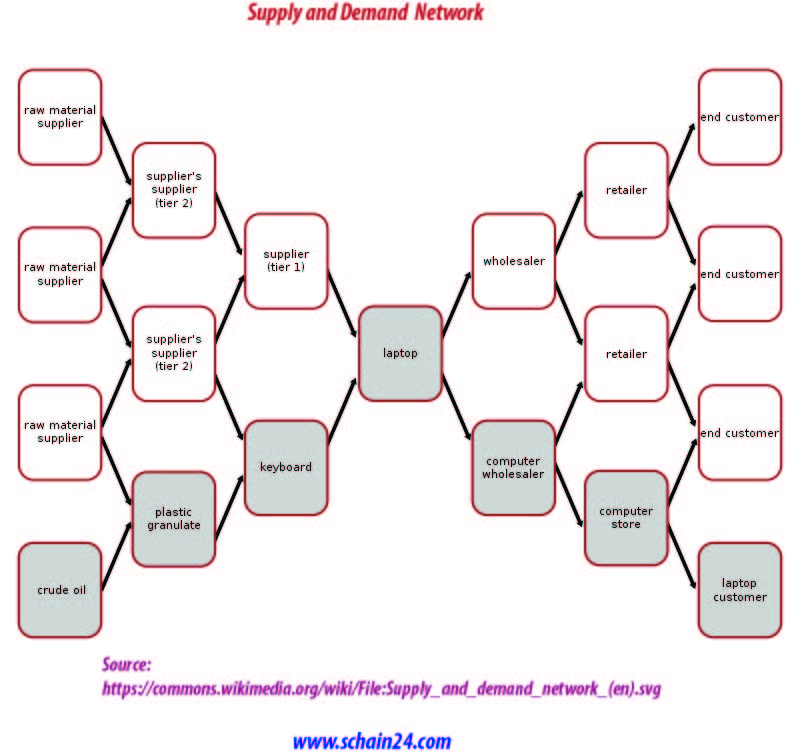
Transportation refers to the movement of things from one point to another as products make their way to reach the customer at the beginning. Supply Chains use responsive transportation to centralize inventory and operate with fewer facilities. The shipper requires the movement of products from one point to another in a Supply Chain and Carrier is the party who moves the cargo. The other parties are owners and operators of roads, ports, canals, and airports and bodies that set transportation policies. A carrier takes investment decisions regarding their equipment; Shipper in contrast uses transportation to minimize total cost, while providing an appropriate level of responsiveness to the customers.
Air vs. Package carriers
Supply Chains using modes of transportation, such as air, package carriers, trucking, rail, water, pipelines, intermodal, etc. The effectiveness of any mode of transportation is affected by the carrier as well as infrastructure and transportation policies, e.g., an airline’s goal is to maximize the daily flying time of a plane and generated revenue per trip. Air carriers usually carry below 500 pounds, high-value, and lightweight products. The Key issues air carriers usually face include identifying the location and a number of hubs, assigning planes to routes, and maintaining a schedule of planes and crews, also available at different prices.
But package carriers, such as DHL, FedEx, UPS, etc. usually carry letters and other small cargo weighing below 150 pounds using air, Truck, and rail to carry time-sensitive smaller packages. They are expensive and cannot go for competition with other carriers for larger shipments due to expense. They can provide other value-added services e.g., speed inventory flow and track order status. Companies use air cargo carriers for
larger cargo and package carriers for more time-sensitive smaller cargo.
The Truck and Rail as a transport
The truck shipment has two types of segments, i.e., TL (Full Truck Load) and LTL(less than Truck Load). It can reach the customer’s door, but it is more costly than Rail transport. The truck has usually a shorter delivery time also. Through consolidation, LTL trucking can reduce costs through consolidation centers products originating from a geographical area and destined to the same geographic area. A key issue for the LTL industry is the location of consolidation centers and the scheduling and routing of pickup and delivery. Rail carriers incur a higher cost including rails, locomotives, cars, and stations/yards. The idle time is more expensive in rail transport. Labor and fuel cost is more than 60% of the total running cost of the train /rail transport. To be profitable, a rail transport crew and locomotives should be well utilized.
The Water Transport
Water transport is ideal for carrying very large loads at low cost. Very large sty shipment in international destinations is carried with comparatively quite low cost.
 |
| A Depiction of a Transport By Water |
Transportation by Pipeline
The pipeline is used for gas and liquid items transportation. In the United States, it is widely used (about 17 % of ton-miles in 2002).
Intermodal Transportation
Some carriers are transporting cargo by using different modes of transportation to go to their destination. The most common is Rail + Truck and Water+ Truck carriers. These types of shipments usually involve great delays in shipments, which lowers costs to some extent.
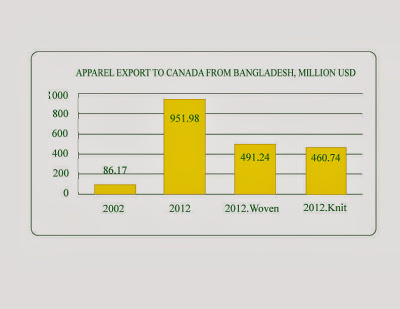
The Perspective of the Bangladesh Apparel Supply Chain
In the last decade, export in Bangladesh has been increased continuously. But due to great competition in the world market, they need to improve their logistics and transportation capability to cope with the competition. The Manufacture of readymade garments in Bangladesh’s export industry using fast, low-cost, and reliable logistics. The industry is subdivided into woven and knitwear. The woven portion is operated as a cut, manufacture, and trim (CMT) process. They need to import fabric, accessories, etc. Whereas knit fabrics need to have a principal import of raw cotton or synthetic fiber.
The woven industry needs a longer time to import fabric. It is rare to do some preprocessing of raw materials, but the knitwear industry can do some pre-processing. Imported fabrics are shipped as CIF. The mother vessel’s movements are mostly predictable. Feeder Vessel’s movements to Chittagong port is about 5 days and unloading takes two-three days. The only uncertainty is taking the fabric to the factory premises, which reaches to factory premises within 1-3 days. Garments are shipped to the buyers generally on FOB terms. The cargo moves from the factory premises to the port in a truck or multi-modal movement of truck and container on the rail. An Ocean movement on a feeder’s vessel to Singapore or Colombo and then by mother vessel to the destination port. By land moves to buyer’s warehouse. If Bangladesh has to compete with other South Asian countries, they have to improve its Supply Chain and can help them in some area such as public-controlled railways, etc and other national policy matters.
Future of Transportation
AI will manage the optimum distance between vehicles, maintain constant communication between vehicles, and plan the formation of vehicle clusters to ensure consistent traffic flow and avoid bottlenecks. AI algorithms can mine historical and real-time traffic data to create predictive models to anticipate traffic congestion and accidents. AI can analyze data on air quality, weather, and traffic patterns to determine the most environmentally friendly routes for autonomous vehicles. This can help in rerouting autonomous vehicles to avoid traffic and optimize travel time. AI algorithms can optimize routes for each autonomous vehicle in real-time, based on traffic data, road conditions, and other factors.AI will play a significant role in controlling autonomous vehicles and managing traffic in the future.
Conclusion
The transportation-related logistical issues are highlighted above with reference to Bangladesh’s situation in reality especially considering the Apparel Supply Chain situation.AI will have a significant impact on autonomous vehicles and the future of transportation, making it safer, more efficient, and environmentally friendly.
References
1.Supply Chain Management: Strategy, Planning, and Operation,By Sunil Chopra & Peter Meindl.
2.https://youtube.com/shorts/Oo2kt5gRWEQ?feature=share
3.https://youtu.be/DiX4OVUC9aI



You may contact with me through contact us page .Thanks.
Whats Happening i am new to this, I stumbled upon this I have found It positively helpful and it has aided me out loads. I am hoping to give a contribution & aid other customers like its aided me. Great job.