Abstract
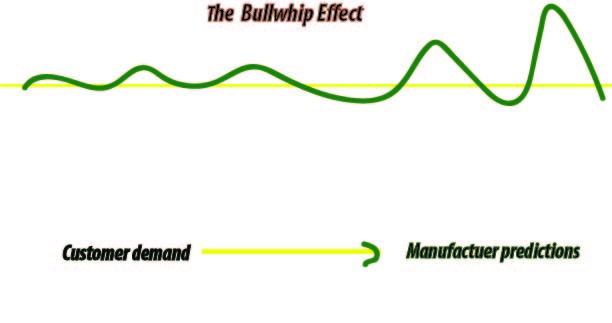
In SCM, a supply chain manager coordinates the logistics of all the aspects of the supply chain which consists of five parts: the plan or strategy, the source of raw materials and services, manufacturing, i.e., productivity and efficiency, delivery and logistics, the return system for defective and unwanted goods etc. The phenomenon that fluctuation in orders increases as one moves up the supply chain from retailers to wholesalers to manufacturers to suppliers is referred to the bullwhip effect. Managers can help achieve coordination in supply chain by aligning goals and incentives across different functions and stages of the supply chain. When supply chain moves from retailers to wholesalers to manufacturers to suppliers, the bullwhip effect occurs. It results in different stages optimizing local objectives instead of total supply chain profits. The bullwhip effect results in costs in the supply chain and decrease in levels of customer service.
Keywords: bullwhip effect, supply chain coordination.
Introduction
Supply chain coordination improves if all stages of the chain take actions that together increase supply chain value and profits. A lack of coordination leads to degraded responsiveness. And increase of cost within a supply chain occurs. Supply chain managers can take some measures that increases coordination in the supply chain.
The supply chain managers
In SCM, a supply chain manager coordinates the logistics of all the aspects of the supply chain which consists of five parts: the plan or strategy, the source of raw materials and services, manufacturing, i.e., productivity and efficiency, delivery and logistics, the return system for defective and unwanted goods etc. The supply chain manager tries to minimize shortages and keep costs down. The job is not only logistics and purchasing inventory, they make recommendations to improve productivity, and efficiency, go straight to bottom life of the company and have a real and lasting impact. Supply Chain Managers need to consider the influence of choosing appropriate forecasting parameters in order to reduce the bullwhip effect.
The example of Ford
When the supply chain stages do not get proper information as it is distorted when moving between the stages. Today supply chains produce a great variety of products. American vehicles producer produces different models and several options. Also having many suppliers and dealers. And have to cope with different ownership and dealers. When supply chain moves from retailers to wholesalers to manufacturers to suppliers, the bullwhip effect occurs. Each stage receives different estimate of what demand is.
Aligning goals and incentives
Managers can help achieve coordination in supply chain by aligning goals and incentives across different functions and stages of the supply chain. Other actions we can summarize as sharing of sales and planning, implementation of single point control of replenishment, improving operations to reduce lead times and lot point control of replenishment, improving operations to reduce lead times and lot sizes. Also they can help taking strategies that limit forward buying and building trust and strategic partnership within the supply chain.
Supply Chain performance
The phenomenon that fluctuation in orders increases as one moves up the supply chain from retailers to wholesalers to manufacturers to suppliers is referred to the bullwhip effect. The bullwhip effect results in costs in the supply chain and decrease in levels of customer service. It moves all parties from the efficient frontier. The ultimate result is nothing but decrease of supply chain profitability.
Lack of coordination
A key obstacle to coordination in the supply chain is misaligned incentives. It results in different stages optimizing local objectives instead of total supply chain profits. Other are such as lack of information sharing and operation inefficiencies leading to large replenishment lead times, sales force incentives. All these things result in forward buying and a lack of trust that coordination difficult.
Different forms of collaboration
Partners may collaborate on store events, DC replenishment, store replenishment or assortment planning. DC replenishment is easier because, it requires aggregate level data. Store replenishment collaboration requires higher investment and data sharing to be successful.
Apparel supply chain bullwhip effect
We could handle the above mentioned effect by taking below mentioned measures.
-Continue to communicate daily with all key people and teams,
-Take accurate inventory of all stocks
-Put orders in now instead of waiting a few weeks to see what you’ll need then.
– Built in delivery delays and logistics disruptions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we can say that in general we can get rid of bullwhip effect Reduced lead times, revision of reordering procedures, better forecasting methods, limitations of price fluctuations, integration of planning and performance measurement. Transportation can play a major role in avoiding the bullwhip effect in your supply chain, depending on how we approach it. We will gain an understanding of both real-time and historical knowledge as it applies to all points in the supply chain through effective communication and data-sharing between all supply chain partners. The better we can make decisions, the better the chances of avoiding the bull.
References
1.Chan.Angela. (2020). “What Fashion Supply Chains Can Do Now to Dodge the ‘Bullwhip Effect”.https://sourcingjournal.com/topics/thought-leadership/coronavirus-fashion-supply-chain-bullwhip-effect-inventory-factories-suppliers-202365/
3.Vazzana.Scott.(2020).”https://info.transportationinsight.com/blog/supply-chain-bullwhip?
4. Alizadeh,Parisa.(2012).”THE ROLE OF FORECASTING PARAMETERS IN
REDUCING BULLWHIP EFFECT”.Advances in Production Engineering & Management, 177-186 ISSN 1854-6250.