Abstract
Society, businesses and governments can all be remodeled in the aftermath of the coronavirus happening, and that we hope, towards a lot of sustainable society, thus, students and managers ought to plan to think about this transformation through a positive lens so as to boost supply chains to produce high worth and even a lot of outstanding services to society, since it’s currently extravagantly clear that supply chains are the veins of the whole economy. In line with UNEC for Latin America estimate, the pandemic-induced recession might leave 14–22 million of individuals in extreme economic condition in Latin America than the scenario while not the pandemic. Lloyd’s of London has calculated that the worldwide insurance trade has to absorb losses of US$204 billion, more extraordinary than the losses from the 2017 Atlantic cyclone season and 9/11, suggesting the COVID-19 pandemic is possibly costliest disaster ever in human history. Governments are possibly to take a position and regulate “key supply chains”, like pharmaceutical, personnel protecting instrumentation and agro-food chains so as to make sure national food security. As of 6 July 2020, over 11.4 million cases of COVID-19 are reported in addition for 188 countries and territories, leading to over 533,000 deaths. On a daily basis a lot of cases are reported, and new countries enter the World Health Organization’s (WHO) list of areas wherever the virus has been reported suggested preventive measures embrace hand washing, covering one’s mouth once coughing, maintaining distance from others, sporting a mask at public settings, and observation and self-isolation for people that suspect they’re infected. The COVID-19 pandemic, referred to as the coronavirus pandemic, is in progress as the global pandemic of coronavirus illness 2019 (COVID 19), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus as a pair of (SARS CoV 2).
Keywords: covid-19, global supply chain, supply chain sustainability, economy.
Article
Introduction:
The Corona virus (Cavid-19) has effects on China’s economy additionally as different elements of the planet. Bangladesh is one of the Asian nations that is among the twenty countries suffering highest from China’s economic problems. This can be seen in the report of UNCTAD, the UN agency for trade and development. From medical instrumentation shortages to panic-buying, the links in supply chains are breaking. However, it can provide valuable learning lessons for the long run.
Covid19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, conjointly referred to as the coronavirus pandemic, is associated in progressing international pandemic of coronavirus illness 2019 (COVID‑19), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus as a pair of (SARS‑CoV‑2). The happening was 1st known in an urban center of China, in December 2019. The World Health Organization(WHO) declared the happening a Public Health Emergency of International Concern on 30th January, 2020, and declared it a pandemic on 11th March,2020. As of 6th July 2020, over 11.4 million cases of COVID-19 are reported in in 188 countries and territories, leading to over 533,000 deaths. Over 6.16 million individuals have recovered. The virus is primarily unfolded between individuals through contacts, most frequently via tiny droplets created by coughing, sneezing, and talking. The droplets typically fall to the bottom or onto surfaces instead of motion through air over long distances.
Contamination of the disease
However, analysis as of June 2020 has shown that speech-generated droplets could stay mobile for tens of minutes. Less normally, individuals could become infected by touching a contaminated surface and so touching their face. it’s most contagious throughout the primary 3 days when the onset of symptoms. Common symptoms embrace fever, cough, fatigue, shortness of breath, and loss of sense of smell. Complications could embrace respiratory disorder and acute respiratory distress syndrome. The time from exposure to onset of symptoms is usually around 5 days however could vary from 2 to 14 days. There’s no known immunogenic or specific antiviral treatment. Primary treatment is symptomatic and appurtenant medical care. Suggested preventive measures embrace hand washing, covering one’s mouth once coughing, maintaining distance from others, sporting a mask in public settings, and observation and self-isolation for people that suspect they’re infected. Authorities worldwide have responded by implementing travel restrictions, lock-downs, geographic point hazard controls, and facility closures. Several places have conjointly worked to extend testing capability and trace contacts of infected persons.
Supply Chain disruption
Every day a lot of cases are reported. New countries enter the World Health Organization’s (WHO) list of areas wherever the virus has found its way. This report discusses the economic impact of the COVID-19 crisis across industries, and countries. The international organization fears that the corona virus might injury Bangladesh’s textile and readymade clothes sector, wood and furniture industries, and animal skin industries. Whereas some countries are ready to treat the reported cases effectively, it’s unsure where and when new cases can emerge. If China’s supply chain loses, the injury to the economies of twenty countries may well be the maximum amount as fifty billion. It conjointly makes an attempt a rough estimate of the potential international economic prices of COVID-19 underneath totally different situations. It seems, however, as if the cases reported from China have peaked, and are currently falling. Countries can suffer, particularly as supply chains are discontinuous.
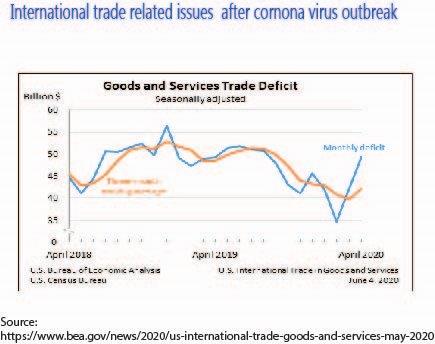
Trade analytics
Trade analytics show China lost global export market share at an accelerated pace in 2019, as companies moved to other countries. Where other countries will benefit from supply chain investments will depend largely on their own investments to boost manufacturing capability as well as provide attractive offerings for land, labor and logistics. Together, the two countries have grown their market across the consumer goods and technology, media, and telecoms (TMT) sectors to 12% and 9% by 2019, largely at the expense of China. The global supply chain had begun responding to US-China tensions and we can expect the disruption caused by COVID-19 to accelerate the pace of this response. At the same time, continued efforts to conclude free trade agreements (FTAs) could further impact where and how businesses seek to restructure their supply chains.
Insurance sector
Lloyd’s of London has calculable that the worldwide insurance trade can absorb losses of US$204 billion, extraordinary the losses from the 2017 Atlantic cyclone season and 9/11, suggesting the COVID-19 pandemic can possible go down in history because the costliest disaster ever in human history. in line with a UN Economic Commission for Latin America estimate, the pandemic-induced recession might leave 14–22 million a lot of individuals in extreme economic condition in Latin America than would are in this scenario while not the pandemic.
The retail sector
The retail sector has been wedged globally, with reduction of work hours or temporary closures. Visits to retailers in Europe and Latin America declined by forty p.c. North American geographical region retailers saw a 50–60 percent drop. Many jobs may well be lost globally. over forty million Americans lost their jobs and filed state insurance claims. On 28th Feb,2020 Scope Ratings GmbH affirmed China’s sovereign credit rating however maintained a Negative Outlook.
Supply chain sustainability
Society, businesses and governments need all be remodeled within the aftermath of the coronavirus happening. We hope that we would go towards a lot of sustainable society. Thus, students and managers ought to plan to think about this transformation through a positive lens so as to produce high worth and even a lot of outstanding services to society, since it has currently been created extravagantly clear that supply chains are the veins of economy. It is possible that governments to take a position and regulate “key supply chains”, like pharmaceutical, personnel protecting instrumentation and agro-food chains so as to make sure national food security. The role of intermediaries may additionally be reassessed because it is thru them that the micro and little farmers could coordinate their actions to provide deeper impact within the supply chain, and end-consumers will shorten the supply chain by being actively concerned in production/distribution systems. We have a tendency to become into a replacement age of localized or regionalized supply chains and government intervention to work. The planet is probably going to ascertain a lot of rough relation between political science and supply chain decision-making processes.
Conclusion
The world gets the pandemic through its start in Wuhan, China. Like other diseases like high blood pressure and diabetes, it is not an individualistic disease. It is by it nature, prevalent over a whole country or even the whole world. It disrupts the supply chain. Due to connected and global nature of the world economy, it heavily changes the pattern of supply chain. Sectors such as insurance, hospitality, retailing industry has got a great setback. Governmental policy regarding regulating supply chain has been changing a lot. Its global nature is no more that much global same as before.
References:
1.Fernandes, Nune. (2020). “Economic effects of coronavirus outbreak (COVID-19) on the world economy”. IESE Business school of Finance. Spain.
2. Jabbour, Ana Beatriz Lopes de Sousa. Jabbour, Charbel Jose Chiappetta. Hingley, Martin. Vilalta-Perdomo, Eliseo Luis. Ramsden, Gary. And Twigg, David. (2020). “Sustainability of supply chains in the wake of the coronavirus (COVID-19/SARS-CoV-2) pandemic: lessons and trends”. University of Lincoln, Lincoln International Business School, Lincoln, UK and Montpellier Business School, Montpellier, France.
3. “Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)—Symptoms and causes”. Mayo Clinic. Retrieved 14 April 2020.
4.https://cutt.ly/0bG9g32
5.Hedwall,Mattias.(2020).”The ongoing impact of COVID-19 on global supply chains”.https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2020/06/ongoing-impact-covid-19-global-supply-chains/