Abstract:
The e-Commerce platform can potentially evolve as a self-managed platform allowing the suppliers to add their products online and buyers to transact on this platform within the constraints defined in the smart contract framework. A block chain-powered solution can provide a robust platform for suppliers and buyers to collaborate and manage an online store. Using block chain for through all steps of the process — proposals, quotes and bids — or auction, can offer greater efficiency and transparency. The smart contracts can be enabled to validate all the rules required for business compliance, regulatory compliance, obligation management and more. The adoption of new technology, tools or techniques should be evaluated based on the savings opportunities and sourcing complexity. All nodes connected to the block chain network receive updated versions of the ledger as new transactions are made.In simple terms, a block chain can be thought of as a secure, public, and external system of record, which participants can inspect, audit, and update. With block chain technology, information at each step of the shipping process is logged in a secure and public database, which cannot be modified by any of the parties involved without it becoming immediately apparent to others. As block chain technology records every single transaction in its ledger, all payments and financial information are available in the public domain. The data which drives this innovation can be taken from manual scanning at shipping centers, or from automatic processes such as temperature sensors within freight containers. Smart contracts are able to automatically find, negotiate, and close deals right across a supply chain, and without the need of a trusted third party. A smart contract is a set of executable code – i.e. a software program – that runs on top of the block chain to carry out the contract.
Keywords: Blockchain, Procurement, E-commerce, Technology, AI, supply chain, logistics etc.
Article:
Introduction:
Importantly, though the technology has earned its fame in the world of cryptocurrency, a blockchain can be programmed to record not only financial transactions, but anything of value, including contracts, records, and other important information. For the uninitiated, a blockchain is a distributed, digital ledger, which allows transactions to be completed on a peer-to-peer basis, with no centralized authorizing agency. In other words, block chain transactions do not require agency, and multiple copies of each transaction may exist in more than one location. All nodes connected to the block chain network receive updated versions of the ledger as new transactions are made.For starters, block chain isn’t really “today’s technology.” The concept has been around for about a decade, and is familiar to most people through association with crypto-currencies like Bitcoin.In simple terms, a block chain can be thought of as a secure, public, and external system of record, which participants can inspect, audit, and update. It can help procurement as discussed below.

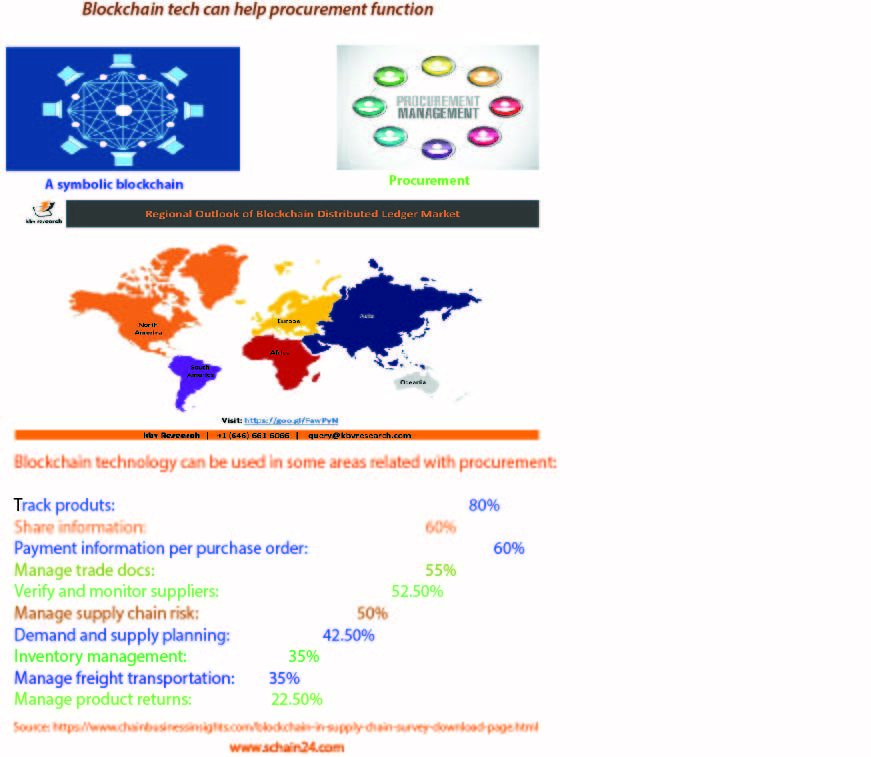
Procurement:
With block chain technology, information at each step of the shipping process is logged in a secure and public database, which cannot be modified by any of the parties involved without it becoming immediately apparent to others. One of the biggest issues in procurement (and in any supply chain system) is ensuring trust and transparency when multiple agents – or even countries – are involved in the various stages of the process. Using block chain technology, any changes made to a ledger are logged, thus ensuring up-to-date information among all systems referencing it. As block chain technology records every single transaction in its ledger, all payments and financial information are available in the public domain. This means, should something go wrong during the shipping process, the supply chain can be traced back to the point at which the mistake occurred. We live in an age where our coworkers are still falling prey to phishing schemes and our third party integrations open the door to supply chain cyberattacks. In short, the danger of calling something hack-proof comes from the false sense of security it emboldens… An impression that could spread to other less invincible realms of our technology landscape. Tracking such problems back to their source could be made easier by reviewing the entries made to the blockchain ledger, and you can be assured that the record is tamper-proof. [1] [2]
Contracts in procurement:
As smart contracts are based on a software program that runs automatically – using information guaranteed by the blockchain to be correct – manual checking of conditions and events by third parties can be avoided, significantly reducing transaction costs and facilitating more advantageous trades.The smart contract will function exactly as it has been programmed, with terms and conditions able to be specified by both sides, ensuring trust in the enforce-ability of the contract, and the identity of the counter-party. A blockchain platform and its smart contract framework coupled with IoT and AI, can help facilitate greater efficiency in compliance and obligation management.AI can help develop smart wizards to build contracts based on responses to specific questions and can further be enabled for pattern recognition to identify changes to standard clauses or introduction of non-standard clauses. Smart contracts are able to automatically find, negotiate, and close deals right across a supply chain, and without the need of a trusted third party.A smart contract is a set of executable code – i.e. a software program – that runs on top of the blockchain to carry out the contract. Examples of Blockchain Being Used in Supply Chains Today Blockchain provides reliability and integrity in a supply chain – there can be no dispute in the chain regarding any transactions because all parties involved have the exact same version of the ledger.When certain conditions are met, the smart contract will automatically deliver a result or trigger an event.On the flip side of the coin, if a condition has not been met – such as timely delivery – a penalty can be triggered. Inefficient contracting can cause inadvertent losses to business, and some of the biggest challenges in contracting is to track compliance and obligations. [1] [3]
Logistics:
An important part of procurement is logistics. IoT in the logistics ecosystem can provide great insights on inventory management, shelf life, storage temperature, delivery routes, real-time tracking of freight and more.A recent example is that of joint venture between IBM and Maersk, who have recognized the potential and embarked on digitizing their global trade and supply chains. Adopting these new technologies and practices is the new normal and early adopter stand to gain in the market place. The logistics industry is an early adopter of AI, IoT and Blockchain, and is already reaping great business benefits. Procurement practices will never be the same and supply chain operations will transform in ways we never imagined. [3]
Procurement strategy and ecommerce:
Supplier bids are collected using online sourcing events, but a large part of the sourcing evaluation and award process is manual in nature.The e-Commerce platform can potentially evolve as a self-managed platform allowing the suppliers to add their products online and buyers to transact on this platform within the constraints defined in the smart contract framework.A blockchain-powered solution can provide a robust platform for suppliers and buyers to collaborate and manage an online store.Using blockchain for through all steps of the process — proposals, quotes and bids — or auction, can offer greater efficiency and transparency.The smart contracts can be enabled to validate all the rules required for business compliance, regulatory compliance, obligation management and more.The adoption of new technology, tools or techniques should be evaluated based on the savings opportunities and sourcing complexity. [3]
Food safety area:
The collaboration aims to improve food tracking in China, and create a standards-based method for collecting data about the origin, safety, and authenticity of food, using blockchain technology to provide real-time traceability throughout the supply chain.The success of the project led to four organizations – Walmart, IBM, Tsinghua University, and Chinese retailer JD.com – forming the Blockchain Food Safety Alliance in December. Unilever, Nestle, Dole, and five other food giants are also using IBM-built blockchains to improve the traceability of foodstuffs such as chicken, chocolate, and bananas. In August last year, Walmart teamed up with IBM to use blockchain to keep track of the pork it sources from China. For example, in the food industry, it’s imperative for watertight records to be kept so products can be traced back to their source.[1]
Spending analysis and transperancy:
Organizations can develop tools to enhance their spend analysis with public domain data — from social media, weather data, demographics, suppliers, competition and logistics to name a few — to help uncover insights that can save money and improve supply chain.With blockchain technology, information at each step of the shipping process is logged in a secure and public database, which cannot be modified by any of the parties involved without it becoming immediately apparent to others. One of the biggest issues in procurement (and in any supply chain system) is ensuring trust and transparency when multiple agents – or even countries – are involved in the various stages of the process.This means, should something go wrong during the shipping process, the supply chain can be traced back to the point at which the mistake occurred. This enhanced transparency not only adds an extra layer of accountability to supply chains, but also mitigates the risks of criminal activity, such as money laundering. As blockchain technology records every single transaction in its ledger, all payments and financial information are available in the public domain.The data which drives this innovation can be taken from manual scanning at shipping centers, or from automatic processes such as temperature sensors within freight containers. This means any suspicious or malicious transactions are incredibly difficult to hide, and can be flagged and dealt with before they can damage the business – both in terms of revenue and reputation.[3]
Conclusion:
It has been found that the blockchain technology like many other technologies help procurement, supply chain logistics. Above discussion sheds some light on these issues based on contemporary literature and practical experience in this area. Here, we need to know that blockchain technology is in discussion by thought leaders last decade.Procurement is a necessary function in a supply chain to give customer a good satisfaction and sending goods and services to their hands. Contracts are a good instrument to complete procurement that is done between suppliers and buyers. But ensuring transparency in this area is important. Where blockchain technology can help. Banks and other orgainizations now using blockchain technology to ensure transparency.Blockchain technology can help the logistics ecosystem also that is discussed above in some detail. Imporatant areas of procurement like food safely can also take help of blockchain technology including other technologies.
References:
1.WBR insights, “Here’s How Blockchain Technology is Revolutionizing the Procurement Industry”. https://procureconwest.wbresearch.com/blockchain-technology-revolutionizing-procurement-industry-ty-u/
2.“Blockchain: What’s In It For Procurement?”. https://www.strategicsourceror.com/2018/09/blockchain-whats-in-it-for-procurement.html
3.Mutagi, Girish.(2018). “Digital transformation: Next Gen procurement and supply chain”. https://www.ibm.com/blogs/blockchain/2018/04/digital-transformation-next-gen-procurement-and-supply-chain/
4.https://www.chainbusinessinsights.com/blockchain-in-supply-chain-survey-download-page.html