Abstract
Gold is insoluble in nitric acid, which dissolves silver and base metals, a property that has long been used to refine gold and to attest the presence of gold in metallic objects, giving elevation to the term acid test.In the past, a gold standard was often implemented as a monetary policy, but gold coins ceased to be minted as a circulating currency in the 1930s, and the world gold standard was forsook for a fiat currency system after 1976.A total of 186,700 tonnes of gold subsists above ground, as of 2015.Gold’s high malleability, ductility, resistance to corrosion and most other chemical reactions, and conductivity of electricity have led to its perpetuated use in corrosion resistant electrical connectors in all types of computerized contrivances, that is the chief industrial use of gold.London Bullion Market Association -the International Trade Sodality represents the market of gold and silver bullion-has additionally developed responsible guidance standards for refiners in line of OECD guidance on Responsible Supply Chains of minerals from conflict affected areas.Compliance with OECD standards require that gold engenderers should publicly promulgate that gold has been extracted in a way does not contribute to human rights abuses or breaches of international humanitarian laws.
Keywords:Supply Chain Management, Gold Supply Chain,OECD,LBMA etc.
Introduction
The major supply chain challenges in countries with gold mining and gold supply chain are supply of low quality products , unreliable and skeptical lead times , inability of farms to maintain international standard , high transportation and violence by the local communities, fluctuation of international market prices etc. Energy, environmental aegis ascendant entities and other institutions should collaborate with mining firms to deal with environmental pollution and matters of inadequate compensation for the communities whose farm lands are eradicated due to mining to address insalubrious conflicts. Fortifying livelihoods of artisanal miners are additionally part of a responsible gold supply chain. Gold miners and refiners need to meet the standard to remain on the accredited list. Which is required to be accepted in the financial markets.
Characteristics of gold
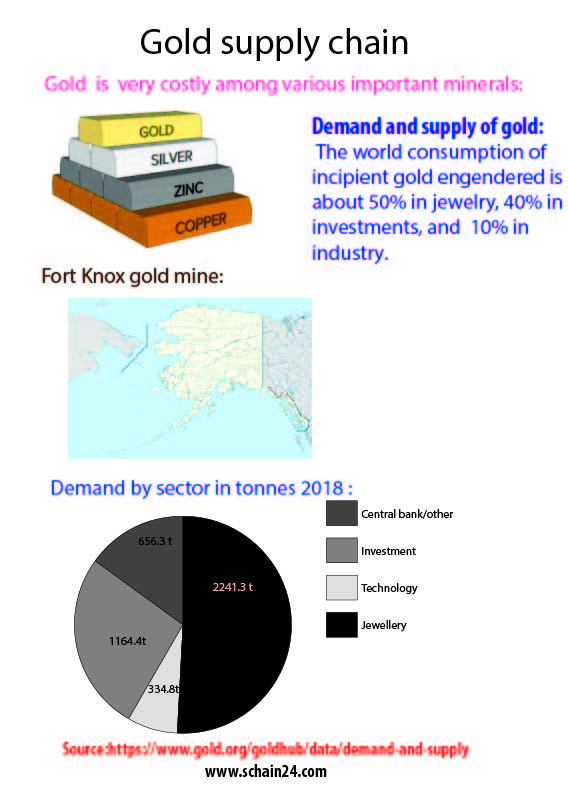
Gold is insoluble in nitric acid, which dissolves silver and base metals, a property that has long been used to refine gold and to attest the presence of gold in metallic objects, giving elevate to the term acid test. In the past, a gold standard was often implemented as a monetary policy, but gold coins ceased to be minted as a circulating currency in the 1930s, and the world gold standard was forsook for a fiat currency system after 1976.A total of 186,700 tonnes of gold subsists above ground, as of 2015. The world consumption of incipient gold engendered is about 50% in jewelry, 40% in investments, and 10% in industry. Gold’s high malleability, ductility, resistance to corrosion and most other chemical reactions, and conductivity of electricity have led to its perpetuated use in corrosion resistant electrical connectors in all types of computerized contrivances, that is the chief industrial use of gold.
Implementation of Gold Supply Chain
There are some guidance available from OECD, which need to be proactively and gradually implemented. Adequate due diligence policy of OECD should be risk-based. Companies document the jeopardy factors and document their decision making about risk factors. And accordingly choose due diligence choices.
Identifying, assessing, reporting, and mitigating risk factors can demonstrate and support plausible efforts. Constructive engagement with suppliers to progressively amend gold supply chain according to standards. It does not intend to provide 100% certainty on conflict free status. And fixates on processes to identify, avert and mitigate risk predicated on available information. They work with suppliers to cut deleterious components of the trade. Industry and multi stake-holders require initiative to assess supply chain circumstances while sharing costs and diminishing the encumbrance of data accumulation.
London Bullion Market Association (LBMA) –the International Trade Sodality represents the market of gold and silver bullion-has additionally developed responsible guidance standards for refiners in line of OECD guidance on Responsible Supply Chains of minerals from conflict affected areas. If refiners are not able to meet the standard gold not being accepted by financial markets. LBMA’s 129 members include trading houses, banks, refiners, miners and fabricators.
Gold extraction strategy
A conflict with the local communities threatens local communities from being benefitted from gold mining. Compliance with OECD standards require that gold engenders should publicly promulgate that gold has been extracted in a way does not contribute to human rights abuses or breaches of international humanitarian laws. There should have a procedure of whistle-blowing, if human rights abuses occur, need to be available for conformance with the standard when operating in a conflict affected area.
Artisanal mining is a way to extract gold. The challenge is that it should be assured that these miners can carry on their working, when this is their only chance to make a living, while additionally protecting the environment and workers from exploitation.
Gold mining economy is auxiliary to people e.g., Ghana, Tanzania, Congo etc. The benefits does not simply benefit those who work in the industries, but additionally spread to local economy. Strategies should avail them to do that. The mining sector, just like other industries coordinate among all members in the supply chain.
Sourcing strategies need to be efficacious and efficient, because gold supply chain is depending on sourcing to an immensely colossal extent.
In a study it is revealed that violence and disputes as well as contingency cognate deaths are prevalent challenges that characterize mining operations in most communities. It is imperative to deal with these challenges.
Countries with technological drawbacks
The African countries like Ghana, Congo etc. are not very much advanced at technological know-how. So they require to have more time to implement the OECD and LBMA standards. In that case, the international communities e.g. OECD and LBMA need to exercise some flexibility to fill up the requisites. And the Financial markets can accept the gold they refine and engender from their mines. And market requisites and supply/demand forecasts are filled up without engendering turmoil in the world gold market and paramount requisites for jewelry, scientific or otherwise.
These countries can go for investors who can develop the technological infrastructure. It is supposed to be good for all parties.
Conclusion
Environmental pollution, employment cognate issues, inadequate emolument paid to owners of land ravaged by mining cognate activities and issues on resettlement are identified as the major sources of dispute that frequently develops between mining organizations and communities. Compliance of OECD and LBMA standards need to be implemented to avail these issues. The International business community can come forward to help the countries who has quandary with technological drawbacks. This will avail the gold requisites in the international market and stabilize the financial market additionally.
Further readings:
1.https://www.theguardian.com/sustainable-business/gallery/challenges-global-gold-supply-chain-pictures
2.http://www.oecd.org/about/
3.http://www.lbma.org.uk/
4.https://www.gold.org/goldhub/data/demand-and-supply